The gut microbiota, a group of microorganisms that reside in the gastrointestinal tract, influence many physiological processes, including immune response, digestion, and even neurological health. It has just been found that gut microbiota has a significant influence on sleep patterns, particularly in newborns.
The Connection Between Gut Microbiota and Baby Sleep Behavior
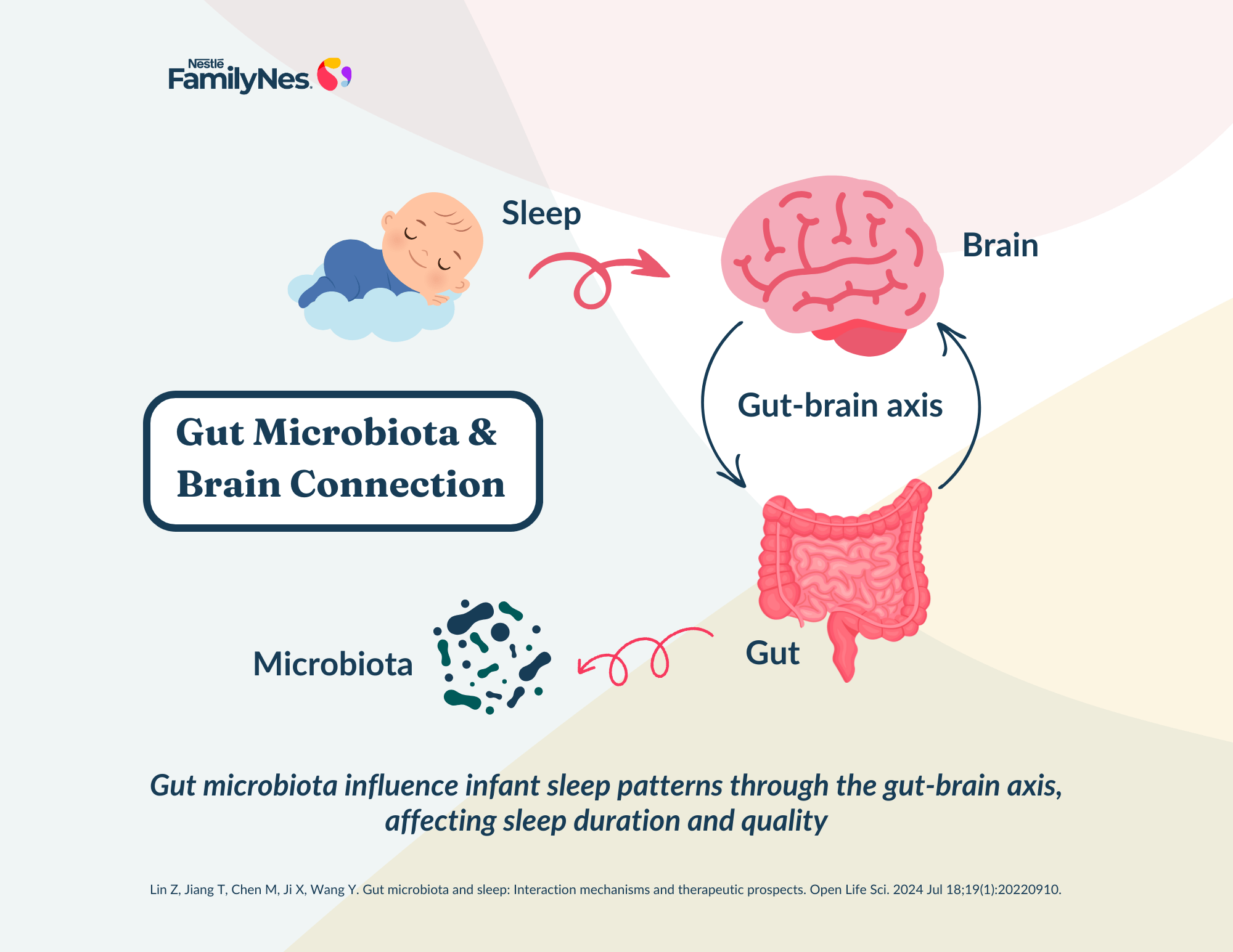
The link between gut microbiota and baby sleep behavior provides valuable insights for new parents. The gut is home to trillions of bacteria that influence digestion, immune function, cognitive development, and even mood and behavior. The gut-brain axis serves as a communication pathway through which gut microbiota influences central nervous system functions, including sleep regulation. Additionally, the gut microbiome can affect the immune system by producing cytokines, which play a role in the body’s response to various factors. An imbalance in gut bacteria may lead to immune reactions that can impact overall well-being.3
A baby’s gut health plays an important role in how they sleep. By the time your baby is three months old, changes in the gut bacteria can affect their sleep patterns. Daytime sleep or afternoon naps accounts for ∼25 % of total sleep time. Babies with less variety in their gut bacteria often sleep more during the day. Particular bacterial profiles, such as alpha diversity, are types of bacteria in the gut, especially with a diverse range that has an impact on the quality of sleep at night, highlighting the delicate regulation of the gut-sleep relationship in early development. Certain gut bacteria produce beneficial compounds such as serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) that support restful sleep, whereas an imbalance in gut flora may contribute to frequent night awakenings. Since both sleep and gut health are essential for cognitive and behavioral growth, maintaining a balanced diet and a healthy routine can help support better baby sleep.1
How the Gut Influences Sleep Patterns
The influence of gut microbiota on sleep is promoted through several biological mechanisms:
1. Neurotransmitter Production:
Two chemicals (neurotransmitters) released from brain cells called serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), essential for controlling sleep, are produced by specific gut bacteria. These compounds derived from microorganisms can impact sleep patterns by affecting the gut-brain axis and the central nervous system.2
2. Circadian Rhythm Regulation:
The gut microbiome influences the baby’s internal clock, which controls their natural sleep-wake cycle. When the microbiome is out of balance, it can disrupt this cycle, leading to problems with sleep quality and duration. (The sleep-wake cycle, or circadian rhythm, is the body’s natural pattern of feeling awake during the day and sleepy at night).3
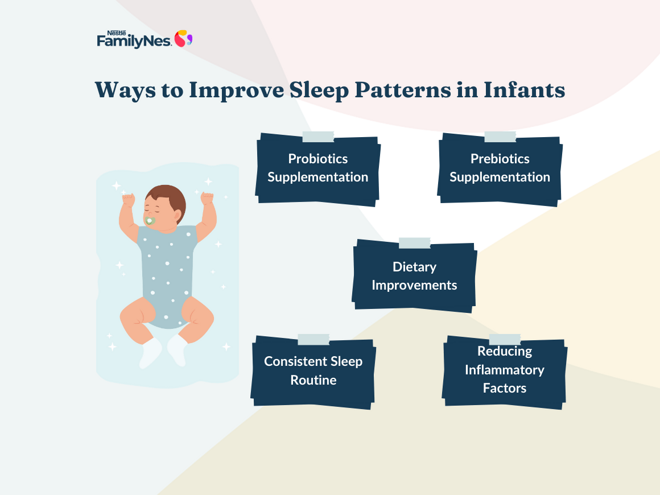
Strategies for Supporting the Fine Balance of Gut Microbiota to Positively Influence Baby Sleep Patterns
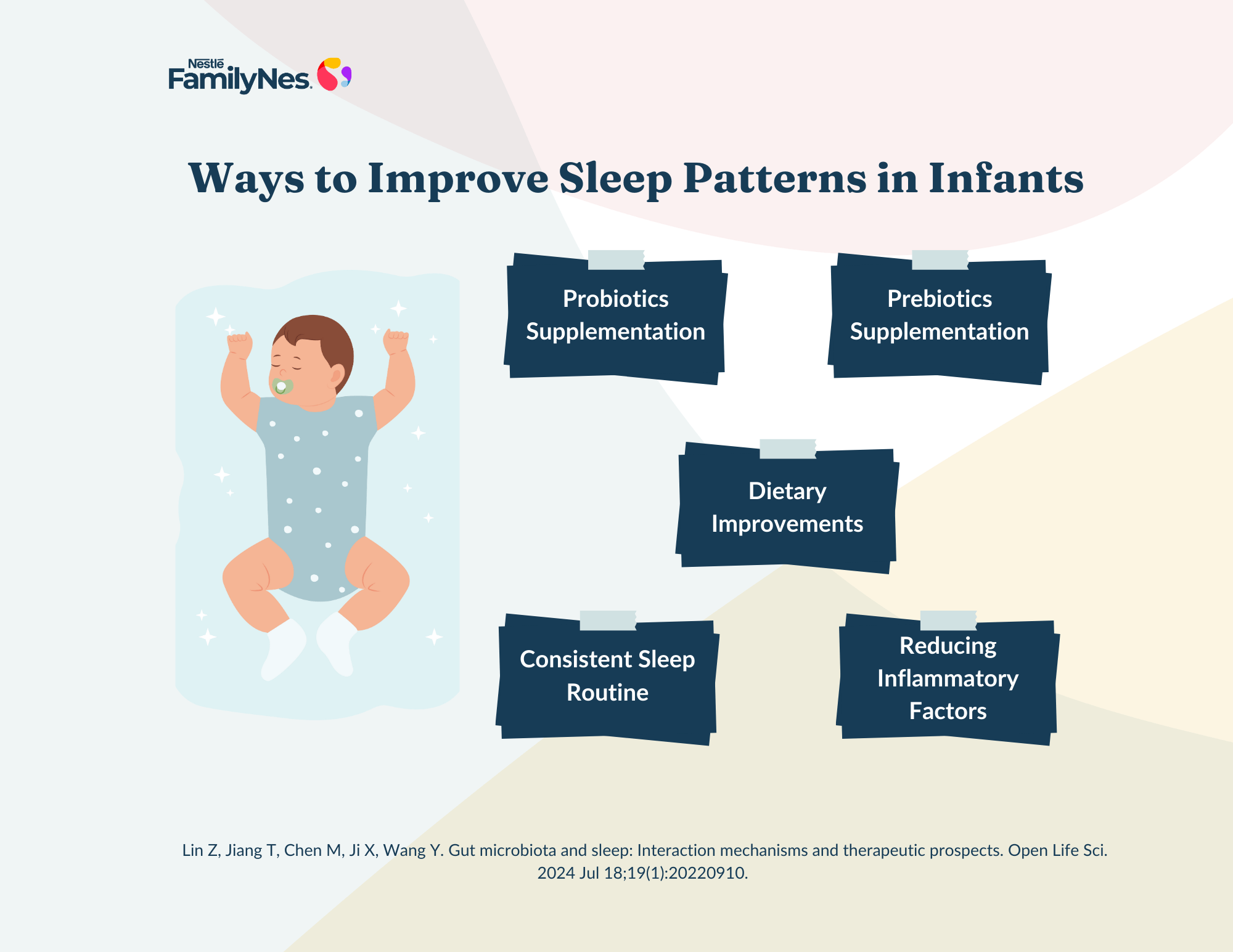
1. Probiotics and Prebiotics:
Certain probiotics (beneficial microbiome) and prebiotics (food of the microbes) can be added to babies' diets to help support development and maintenance of a healthy gut microbiome, which may positively influence the quality of their sleep.3
2. Dietary Improvements:
Healthy gut bacteria could help increase the production of propionate, a beneficial compound that supports gut health and promotes better sleep. Essentially, adding these foods to your baby’s diet could support better sleep by encouraging the growth of bacteria that produce sleep-promoting compounds. Introducing fiber-rich solid foods at the right age can help improve the variety of good bacteria in the gut, which may lead to better sleep quality and longer sleep.3,4
3. Reducing Inflammatory Factors:
An imbalance in good and bad gut microbiota bacteria can lead to inflammation, which has been connected to disrupted sleep in babies. Avoiding overuse of antibiotics and providing a healthy balanced diet rich in probiotics/ prebiotics can help maintain your baby's gut health and support sleep regulation.4
4. Establishing a Consistent Sleep Routine:
Other than appropriate nutrition, the entire environment of the child also influences his/her sleep. A stable bedtime routine, including activities like reducing noise & dimming lights, can regulate circadian rhythms and support sleep efficiency.5
The interaction between gut microbiota & baby sleep plays an important role in the overall quality of life of babies, parents, and caregivers, highlighting the importance of an overall approach to baby health. By nurturing your baby’s microbiome through thoughtful dietary choices, reducing inflammation, and establishing a calm sleep routine, parents can help foster better sleep and, in turn, support their baby’s growth, development, and overall well-being. Understanding and supporting this gut-sleep connection offers a holistic pathway to a healthier, happier start in life.
This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Please consult your healthcare professional
References
- Schoch SF, Castro-Mejía JL, Krych L, Leng B, Kot W, Kohler M, et al. From Alpha Diversity to Zzz: Interactions among sleep, the brain, and gut microbiota in the first year of life. Progress in Neurobiology. 2022 Feb;209:102208.
- Han M, Yuan S, Zhang J. The interplay between sleep and gut microbiota. Brain Research Bulletin. 2022 Mar 1;180:131–46.
- Lin Z, Jiang T, Chen M, Ji X, Wang Y. Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Open Life Sci. 2024 Jul 18;19(1):20220910.
- Sejbuk M, Siebieszuk A, Witkowska AM. The Role of Gut Microbiome in Sleep Quality and Health: Dietary Strategies for Microbiota Support. Nutrients. 2024 Jul 13;16(14):2259.
- Bedtime routines for young children: a dose-dependent association with sleep outcomes - PubMed [Internet]. [cited 2025 Feb 26]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25325483/


